
WordPress is a free, open-source, and free content management system (CMS). It allows the editing of rich and dynamic websites, and benefits from an important ecosystem of plugins and themes. According to wordpress.org, 43% of websites are based on the WordPress CMS.
It is therefore no surprise that WordPress is a prime target for hackers: poorly configured websites and servers, vulnerable plugins, delayed updates.
This article focuses on quick and easy techniques to test yourself if your WordPress site can be attacked by newbies. Above all, it does not replace a hardening of the security of your website.
These tests are intrusive and should be run on systems that you own or for which you have been given explicit permission.
1. Using wpscan
The wpscan tool is an easy-to-use WordPress configuration flaw and vulnerability scanner. It is included in the Kali Linux distribution but can also be easily used separately thanks to its docker image.
In order to benefit from all the functionalities of wpscan it is preferable to create an API key on WPScan.com. This step is optional but allows you to benefit from the WordPress vulnerabilities database.
Here are some examples of wpscan commands to detect a maximum of WordPress vulnerabilities and misconfigurations:
# Default scan of https://your.site.wordpress/ with a random User-Agent and no HTTPS certificate verification (in case you haven’t installed it yet)
wpscan –rua –api-token {TOKEN} –disable-tls-checks –url https://your.website.wordpress/
# More comprehensive scan: Lists top 50 WordPress users, all known themes and plugins, configuration backups, timthumbs and exports. Random User-Agent and no HTTPS certificate verification.
wpscan –rua –api-token {TOKEN} –disable-tls-checks -e u1-50,m,vp,vt,tt,cb,dbe –url https://your.website.wordpress/
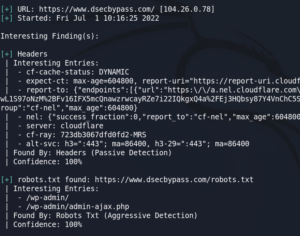
The wpscan results are composed of different categories and offer links to documentation each time:
- At the beginning you will find configuration faults, things that stands out, and general information
- Then there is the version of WordPress if detected, with its possible vulnerabilities
- Discovered plugins and their vulnerabilities
- The same with WordPress themes
- And finally the list of backups, exports, timthumb, media and users
2. Manual additional checks
Although wpscan can trace a large number of WordPress vulnerabilities, a few additional manual tests can eliminate some common weaknesses.
❌ WordPress directory listing
Test accessing the /wp-content/, /wp-content/uploads/, /wp-includes/ directories in your web browser. For example https://your.website.wordpress/wp-content/uploads/. The list of files and folders should not appear!
❌ Obvious passwords
If you have access to the list of users of your WordPress site (https://your.site.wordpress/wp-admin/users.php) or several accounts have been discovered by wpscan, try one or two passwords obvious: username, company name, site/blog name. Be careful not to make too many attempts, you could block your accounts.
❌ Log files indexed by Google
WordPress log files may be indexed by Google. These log files sometimes leak sensitive information. To detect them, the following Google search can be used (Google Dork):
inurl:log -intext:log ext:log inurl:wp- site:your.website.wordpress
💡 Other vulnerabilities and misconfigurations require the skills of cybersecurity experts (pentesters) to be detected and exploited. An intrusion test can reveal all these weaknesses and guide you in their remediation.
🛡️ DSecBypass supports you on the security audits of your websites, in particular the WordPress security audits. Do not hesitate to contact us for additional information and/or a personalized quote 📝.
